Sophos Firewall v21: New functions and improvements
The Sophos Firewall v21 is officially available since October 17th and in this article we describe the new features of this version.
⚠️ Update to Sophos Firewall v21
- ✅ XGS Appliances
- ✅ Install Sophos Firewall VMs or software
- ❌ XG Appliances
- ❌ SG appliances with Sophos Firewall OS
The update to Sophos Firewall v21 is only available for XGS appliances as well as VM and software firewalls. XG appliances and SG appliances with SFOS will no longer receive this update and will reach End-of-Life (EOL) on March 31, 2025. All those affected by End-of-Life will be informed about all details in the XG End-of-Life article.
Topics
Let’s Encrypt
With version 21 of Sophos Firewall, you can use Let’s Encrypt to obtain, renew and manage SSL/TLS certificates automatically and free of charge. The integration of Let’s Encrypt into Sophos Firewall v21 makes it easier to manage certificates and ensures that they are automatically renewed in good time before they expire.
FINALLY! This has probably been one of the most requested features for years and Sophos has taken a really long time here, although FortiGate has also been able to do this for over a year 🫣.
Automatic certificate creation
The Let’s Encrypt certificates are valid for 90 days and are automatically renewed by Sophos Firewall 30 days before they expire. This significantly reduces the manual effort required for certificate management and ensures that the firewall always works with valid certificates.
Supported interfaces
Let’s Encrypt certificates can be used in the firewall for various web services:
- Web Admin Console
- User portal
- Captive Portal
- VPN Portal
- SPX portal
- WAF (Web Application Firewall)
However, Let’s Encrypt is not supported for the following services:
- Remote Access VPN
- Site-to-Site VPN
- Chromebook SSO
Domain validation via HTTP
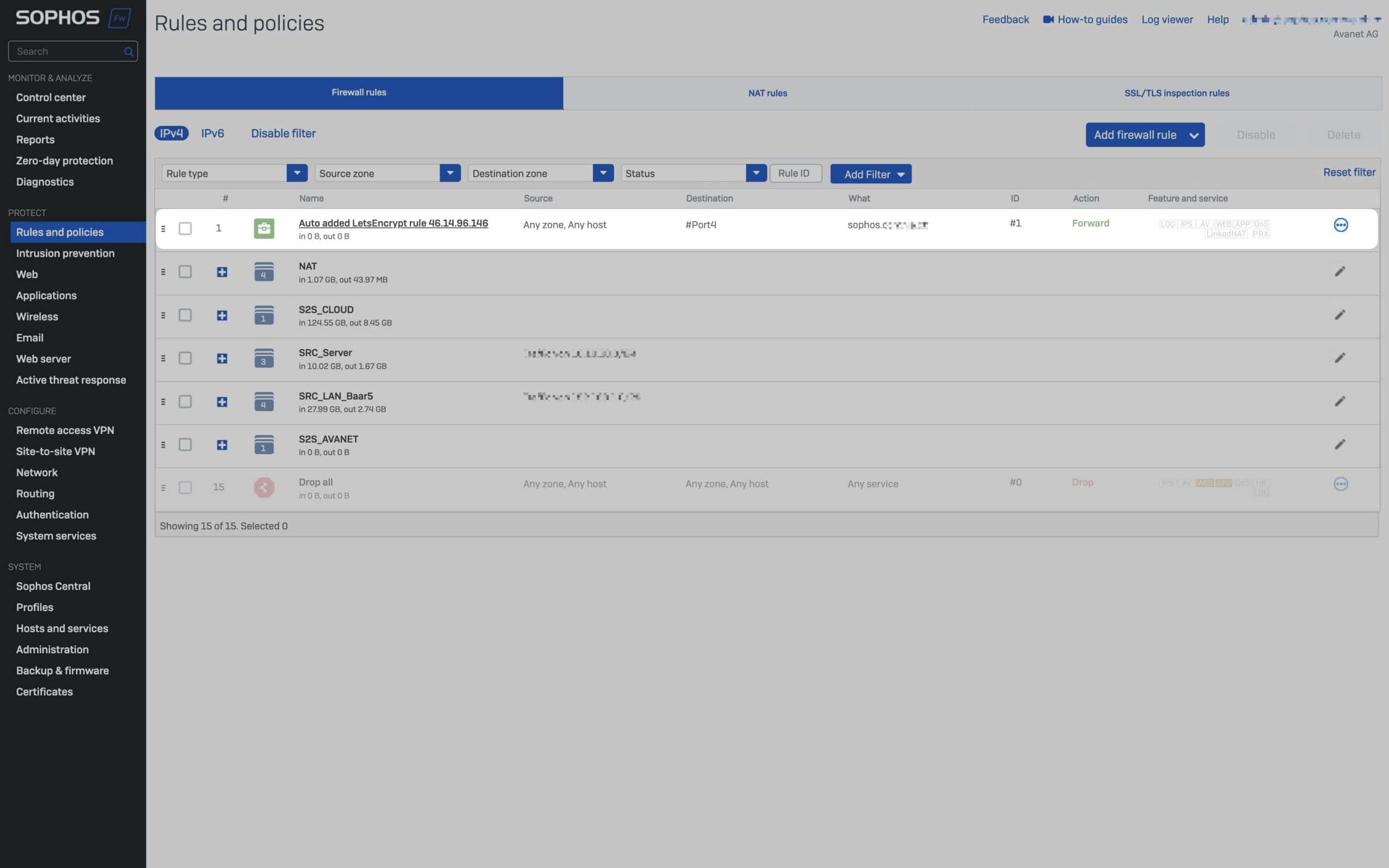
The certificates are validated via the HTTP challenge-response mechanism. The firewall creates a temporary web server configuration and a WAF policy to handle the challenge and validate the domain. The temporary firewall rules and the virtual web server are automatically removed again once the certificate has been successfully issued.
Domain management
You can request certificates for up to 50 domains, whereby only fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) are supported. Wildcard domains and IP addresses are not permitted.
Use Let’s Encrypt certificates
To create a Let’s Encrypt certificate, register an account with Let’s Encrypt in the firewall, add the desired domains and configure the WAN interface for HTTP domain validation via port 80. It is important that the DNS entries point to the public IP of the firewall.
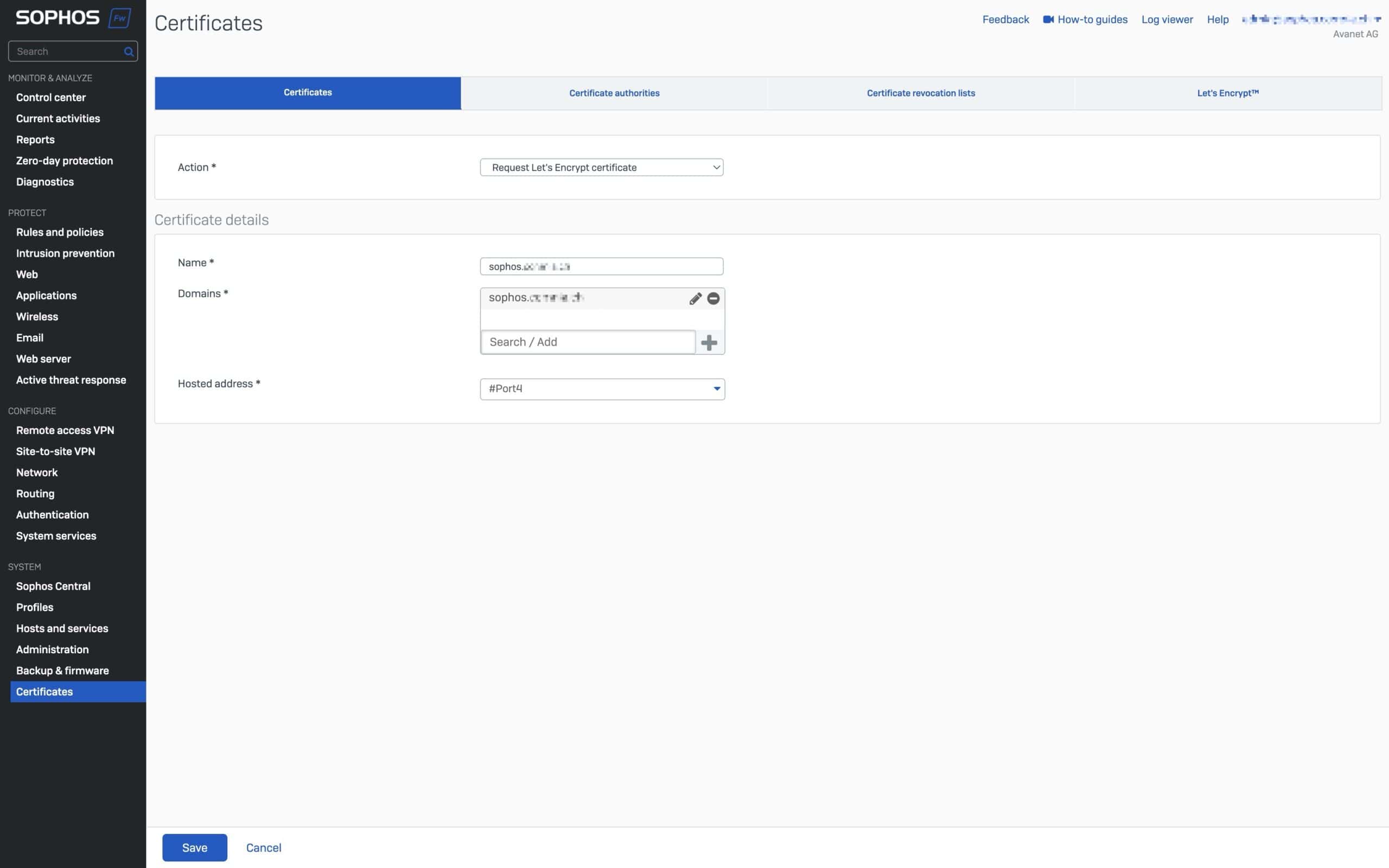
The issued certificates can then be used for the WebAdmin console, user portals and the Web Application Firewall (WAF) to ensure secure HTTPS connections.
Detailed instructions can be found in this video:
UX and UI improvements
Central UI now on firewall
With the update to Sophos Firewall v21, the user interface has been redesigned to improve navigation and data overview. The new sidebar and the adjusted color scheme provide a clearer structure. The dashboard now makes better use of the available screen space by scaling to a width of up to 1920 pixels. This allows more information to be displayed at the same time, making it easier to get an overview.
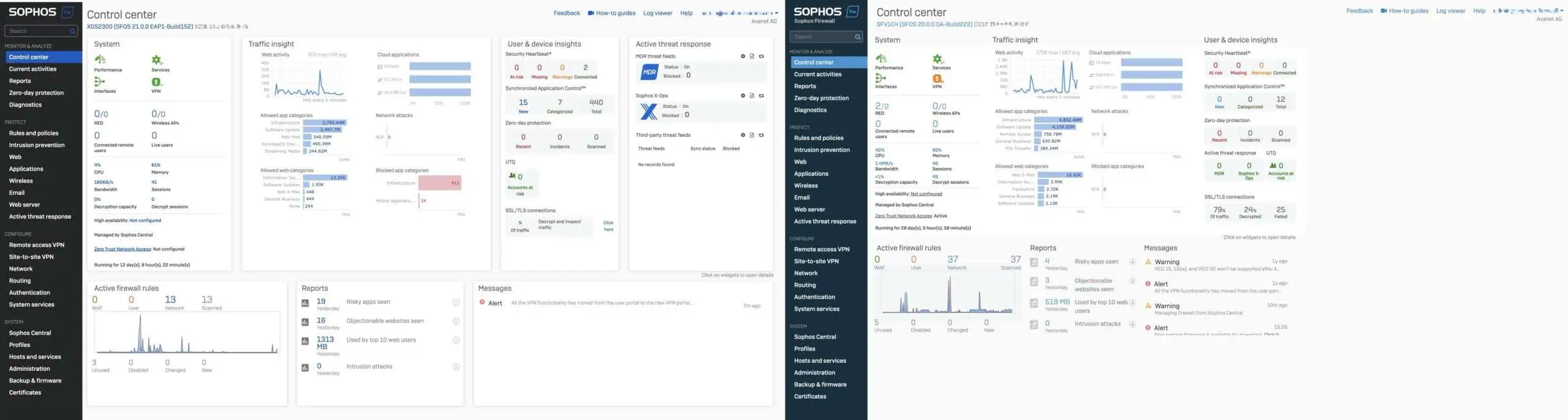
The widgets have also been adapted to make more information accessible at a glance. The map display simplifies the separation of the various data categories. These changes make it possible to access safety-relevant information and system status messages more quickly.
Overall, the revised interface aims to make interaction with the firewall more efficient and it is of course nice to see that Sophos is finally doing something in this area again. I hope the issues of hiding warning messages in the dashboard and backend performance will also be addressed soon.
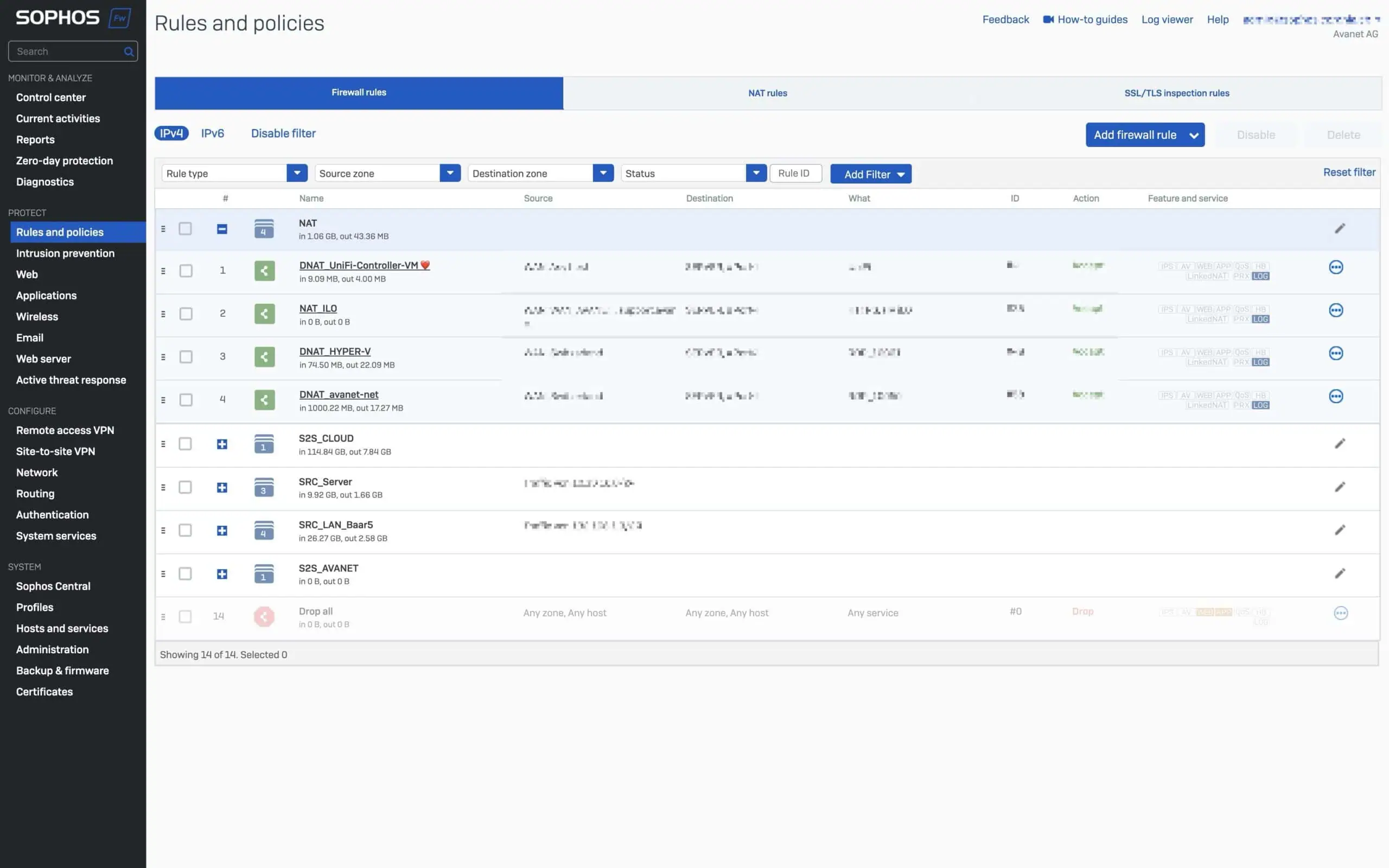
Object referencing
The object referencing feature has been added to Sophos Firewall with v20.
Sophos Firewall v21 provides a way to track the use of objects such as interfaces, zones, gateways or SD-WAN profiles in the configuration. Changes to an object can be made in a targeted manner thanks to the transparency of the usage locations. It is also easier to clean up objects that are no longer in use, as you can quickly see whether they are still in use or can be removed.
Object Reference API
The Object Reference API introduced in Sophos Firewall v21 makes it possible to automatically retrieve the usage count of configuration objects. The API can be used to quickly get an overview of how often an object is used in the configuration. This is particularly useful if you have to manage a large number of hosts or interfaces.
The API enables a programmatic query of the reference count and supports filter options to search for specific objects. This functionality provides an efficient way to identify and, if necessary, remove unused objects. The API can also be integrated into automation processes, which saves time for recurring tasks such as system cleanup.
Third-party threat feeds
Sophos Firewall v21 supports the integration of third-party threat feeds for automated threat defense. This feature extends the existing threat intelligence integration of Sophos X-Ops and Sophos MDR with external threat data sources. Sophos Firewall can now automatically process threat indicators from third-party vendors, managed service providers (MSPs) or industry-specific consortia and block threats in various subsystems.
Automated blocking
As soon as threat indicators are provided by a third-party feed, they are automatically integrated into the firewall rules. Threats such as malicious IP addresses, domains and URLs are immediately blocked on all relevant security modules – including the firewall itself, IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), DNS blocklists, web filters and Deep Packet Inspection (DPI).
Polling interval
The frequency at which the firewall updates the feeds can be set flexibly. Administrators can set the interval between one hour and up to 30 days. This makes it possible to control the updating of threat data as required.
Support for multiple feeds
Sophos Firewall can manage up to 50 different threat feed sources. These feeds must be in a specific format – each Indicator of Compromise (IOC) is transmitted as a single line in a .txt file over HTTPS.
Authentication and security
The integration of external threat feeds usually requires authentication. Sophos Firewall supports various authentication methods, including basic authentication and token-based authentication. This ensures that only authorized threat data sources are used.
Support for external feeds significantly improves the firewall’s defensive capabilities. Threats from industry-specific or regional feeds can be detected and blocked without the need to manually create additional firewall rules.
Threat Feeds Provider
Here is a small selection of providers who make threat feeds available.
CrowdSec
CrowdSec is an open source cyber threat defense solution powered by crowd intelligence. It provides automated blocklists and threat feeds collected from a global community. CrowdSec helps to identify and block threats in real time by aggregating threat intelligence from many participants.
GreyNoise
GreyNoise focuses on analyzing “internet noise” by examining global network traffic to identify which activities are likely to be malicious. It filters out malicious network traffic that is not a direct attack on your infrastructure, helping to reduce false positives and prioritize real threats.
Cisco Talos
Talos is Cisco’s threat research unit and provides one of the largest commercial threat intelligence feeds in the world. It includes detailed information on global threats, vulnerabilities and attackers. Talos supports the detection and defense of cyber attacks with up-to-date threat data.
Abuse.ch / URLhaus
Abuse.ch is a platform that specializes in detecting and blocking malicious domains and IP addresses, especially malware and botnets. URLhaus is an Abuse.ch project that focuses on reporting and blocking URLs that spread malware.
Hakk Solutions
Hakk Solutions is a security intelligence and services provider specializing in threat intelligence and security monitoring. The services include threat data that can be used to identify and defend against cyber attacks.
OSINT (Open-source Intelligence) / DigitalSide
DigitalSide provides open source intelligence feeds (OSINT) based on publicly available information. These feeds contain data on malicious IP addresses, URLs and domains collected from various publicly available sources.
CINS Score (CINSscore.com)
CINS Score provides threat intelligence based on network traffic analysis to help identify malicious hosts and networks. It uses machine learning and heuristic algorithms to evaluate potentially dangerous IP addresses.
EclecticIQ
EclecticIQ provides threat intelligence and analytics for organizations and security operations. The provider offers comprehensive threat intelligence services that make it possible to detect and respond to threats.
Feodo Tracker
Feodo Tracker is another Abuse.ch project that specializes in tracking botnets, particularly Feodo, Dridex and Emotet. It provides information about the servers that these botnets use to control them, helping to identify and block malicious activity.
DigitalSlide Threat Intel
DigitalSide provides threat intelligence feeds with a focus on open source intelligence (OSINT). It collects publicly available information on malicious IP addresses, domains and URLs. These feeds are particularly useful for identifying threats at an early stage as they are based on a wide range of publicly available data sources and are updated regularly.
Proofepoint – Emerging Threat Intelligence
Proofpoint provides comprehensive threat intelligence through its Emerging Threats Intelligence Feed. This service focuses on providing real-time updates on emerging threats, including new attack techniques and vulnerabilities. Proofpoint uses machine learning and expert analysis to provide detailed insights into global threats that help organizations respond to cyberattacks in a targeted manner.
Endpoint threat indicators
Sophos Firewall v21 provides the ability to integrate and analyze threat indicators Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) from endpoints. Both managed and unmanaged endpoints are supported. As soon as an endpoint detects malicious activity, this information is transmitted to the firewall. The firewall analyzes these IoCs and blocks suspicious activity.
This function is particularly useful for improving synchronization between endpoints and the firewall. Threat attempts detected on the endpoints can thus be stopped directly across the entire network. This real-time analysis contributes to a rapid response to threats and the containment of attacks.
Synchronized telemetry
The firewall is able to correlate threat attempts from endpoints by including details such as running processes and applications. This improves threat detection and analysis. As soon as an endpoint detects suspicious activity, this information is automatically transmitted to the firewall to block the threat across different network layers.
Automatic blocking of threats
If a malicious process is detected on a managed endpoint, the firewall automatically blocks the associated IP address, domain or URL. This applies to subsystems such as the firewall, DNS blocklists, web filters and deep packet inspection. This seamless integration between the firewall and endpoints significantly reduces the response time to threats.
An example would be an unmanaged endpoint attempting to access a malicious URL. The firewall would immediately intervene and block access without the endpoint itself requiring any special configurations. This also protects devices that are not directly managed by Sophos Endpoint Security.
The ability to process IoCs from endpoints provides administrators with an additional layer of defense, as the firewall responds not only to network traffic, but also to detailed threat information from the endpoints themselves.
Lateral Movement Protection
Lateral Movement Protection is mentioned again in Sophos Firewall v21, as significant improvements and optimizations have been made in this version. In v21, integration and coordination with other security features such as Synchronized Security and Active Threat Response (ATR) has been improved. The firewall can now respond faster and more efficiently to threats by automatically isolating compromised devices and blocking the spread of threats across the network.
Lateral Movement Protection prevents threats from spreading across the network by isolating compromised devices. As soon as an endpoint is detected as compromised, communication with other devices in the network is blocked. The firewall also shares this information with other endpoints, which then also block network access to the compromised device.
This feature increases security across the network by preventing threats from moving horizontally from one device to the next. It is particularly useful in large networks where the rapid isolation of infected devices can be crucial in preventing an incident.
MAC address blocking
If an endpoint is detected as compromised, the firewall shares the MAC address of this device with all other endpoints in the network. The endpoints then block network access to the infected device. This ensures that threats cannot spread further in the network.
Heartbeat status
The firewall continuously monitors the heartbeat status of the endpoints. As soon as an endpoint is identified as compromised, the heartbeat status changes to red, which triggers an immediate blocking mechanism. The communication of the compromised endpoint is immediately interrupted, enabling effective containment of the threat.
A typical scenario would be an endpoint that attempts to move laterally in the network after it has been compromised. With Lateral Movement Protection enabled, this endpoint is immediately isolated and its communication blocked. This prevents the spread of malware, such as ransomware, which could attempt to infect other devices.
A prerequisite for this function is that the firewall and the Sophos endpoints are connected via Sophos Central. This enables synchronization between the security solutions and ensures that threats can be detected and isolated quickly.
Threats and IoC reporting
Sophos Firewall v21, like previous versions, offers reporting capabilities that are available both on the device (OnBox) and in the cloud via Sophos Central. These reports make it possible to analyze threats and network activities in detail and provide valuable insights into the security situation of the network.
In Sophos Firewall v21, reporting capabilities have been enhanced with the integration of Threat Sources and Threat Events and support for Synchronized Indicators of Compromise (IoC). What is new is that reports now provide detailed information on the sources of threats and their specific events. You can now accurately track threat attempts by seeing which devices, IP addresses or users were involved and which firewall modules blocked the threat.
Particularly noteworthy is the support for Synchronized IoCs. This synchronizes threat data from Sophos Central and Sophos Managed Detection and Response (MDR) as well as third-party feeds. This extension makes it possible to gain deeper insights into threats by analyzing the affected processes and endpoints in more detail. This allows administrators to see not only where threats have occurred, but also how they affect endpoints and network components.
In this video, we explain the topic of third-party threat feeds in detail:
Static route and VPN improvements
VPN UX improvements
Version 21 of Sophos Firewall introduces several improvements to the user interface (UX) for managing VPN connections to make it more efficient to use.
Bulk activation and deactivation
Administrators can now activate or deactivate several VPN connections at the same time.
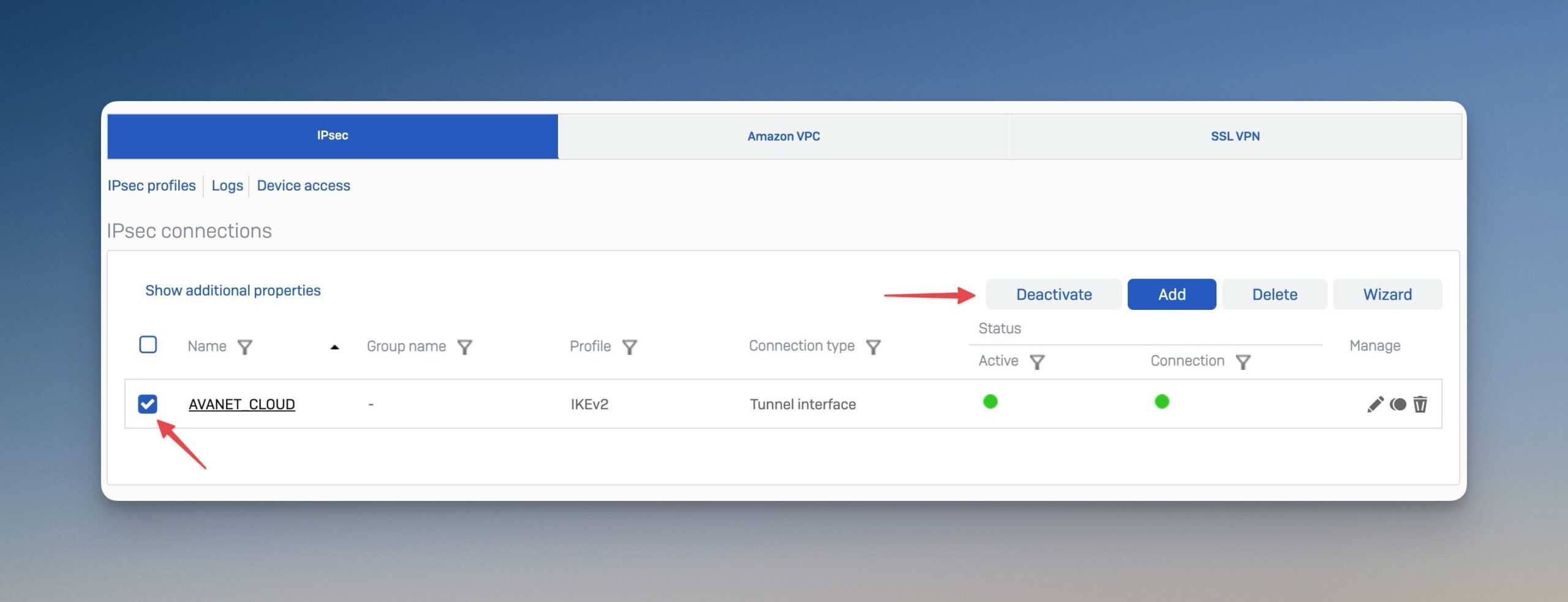
This saves a considerable amount of time, especially when managing large networks with many VPN tunnels. Deactivation is done quickly via a central button in the VPN management area.
Extended filter options
The VPN connections overview page now has improved filtering capabilities that make it easier to navigate through multiple pages of VPN configurations. These filters include both free text entry and value-based search options, making it easier to manage and search for specific networks, subnets or users for remote access and site-to-site VPNs.
XFRM interface filter
An additional filter option for XFRM interfaces has been added. XFRM interfaces that are often used in VPN configurations can now be identified and managed more easily. This is particularly useful when VPNs are set up via VLANs and WAN interfaces.
Site-to-Site VPN
Sophos Firewall v21 introduces several improvements for site-to-site VPNs, focusing on both usability and performance.
DHCP relay via XFRM tunnel: One of the key new features is the support of DHCP relays via XFRM tunnels. This makes it possible to reach DHCP servers behind remote firewalls, which was previously only possible via policy-based VPNs. This is particularly useful in SD-WAN environments where dynamic IP addresses need to be provided via tunnels.
Improved FQDN support: When configuring remote gateways in IPsec VPNs, both FQDNs (Fully Qualified Domain Names) and their resolved IP addresses can now be used. This improves scalability, especially in environments with high DNS latency, where FQDN resolutions could affect the performance of VPN connections. Administrators can choose whether to use FQDNs or resolved IP addresses in the configuration.
The new functions in the site-to-site VPN area provide more flexibility and improve scalability in larger, distributed networks. The optimization of the interface recovery time, which is up to 20 times faster, also drastically reduces downtime in the event of tunnel failures, restarts or HA failover scenarios.
Route Management
Routing management in Sophos Firewall v21 has been enhanced with new features and improvements to simplify the management of static and dynamic routes and increase network stability.
Static routes
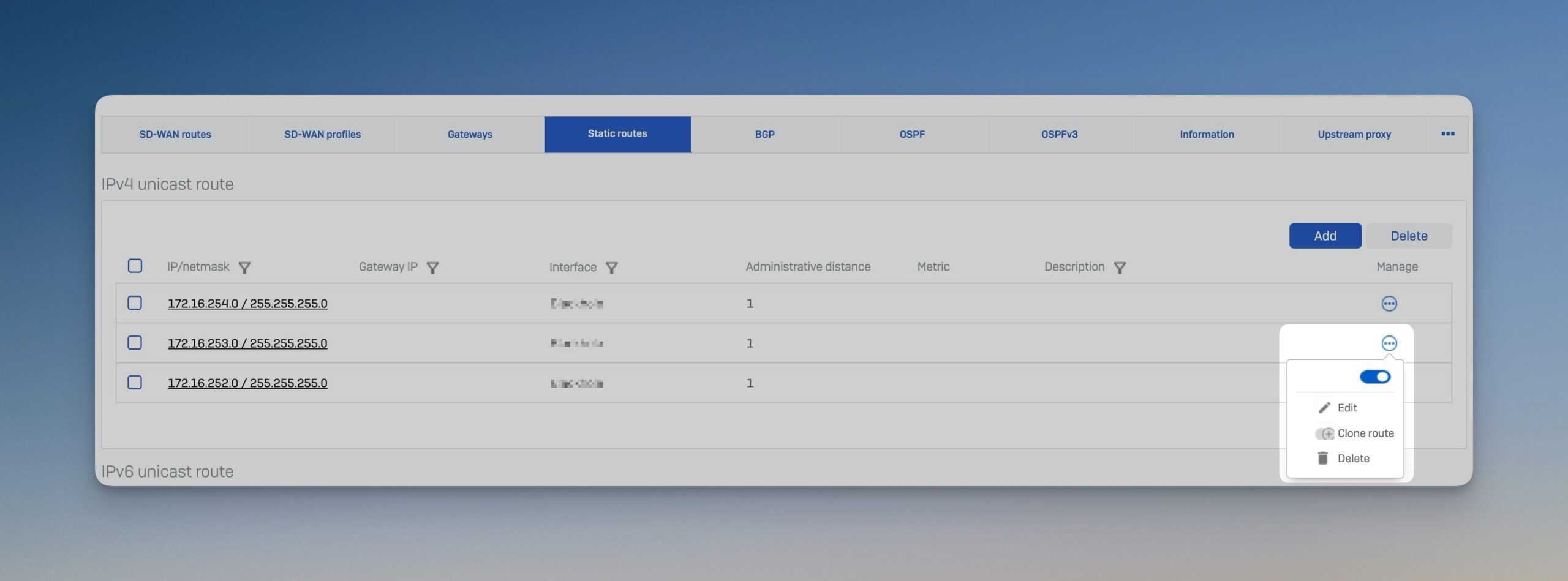
Activation/deactivation of routes
Administrators can now activate or deactivate individual routes directly, which makes troubleshooting and managing network connections much easier. This enables precise control over routing behavior in real time.
Route cloning
With the new route cloning function, existing routes can be easily duplicated and adapted. This saves time during configuration and ensures consistency across different network interfaces. In addition, each route can be provided with a description to increase clarity.
Dynamic routes
Extended support for OSPF and BGP
The firewall now supports forwarding BGP routes to OSPF v3, which improves interoperability between different routing protocols. This is particularly useful in complex networks with multiple locations and protocols.
HA improvements
In high-availability (HA) failover scenarios, the stability of dynamic routes has been significantly improved. Whereas in previous versions there could be several connection failures during failover, this now only occurs once, which increases the reliability of the network connections.
This video summarizes the new features relating to VPN and routing:
Google Authentication
Support for Google Authentication has been extended in Sophos Firewall v21 to facilitate the integration of Google Workspace and Chromebooks.
LDAP-based integration
Sophos Firewall now supports the integration of Google Workspace via a regular LDAP client. This extension makes it easier for organizations that rely on Google Workspace to authenticate their users via Sophos Firewall without having to rely on Active Directory. Support for Google Workspace SSO (Single Sign-On) will also follow in future versions.
Chromebook SSO support
The firewall now offers SSO (single sign-on) functionality for Google Chromebooks connected to LDAP servers. This functionality was previously limited to Active Directory. This allows Google users to access secured resources without additional login steps.
Improved SSO performance
Authentication has been improved so that the firewall can process requests from multiple SSO mechanisms (e.g. STAS, RADIUS SSO, Synchronized User ID) more efficiently. In environments with a high number of concurrent requests, the Server can now respond up to four times faster to authentication requests and discard duplicate requests once a user is authenticated.
Last words
Overall, Sophos Firewall v21 is a solid annual update that brings small but important improvements to the UX and UI, as well as new features that further enhance network security.
We are happy to continue collecting your feedback on which features you currently miss. We have already summarized many of your suggestions in the Sophos Firewall Feature Request 2024 post and are already working on the list for 2025. You are welcome to send us further requests and suggestions via the contact form.







